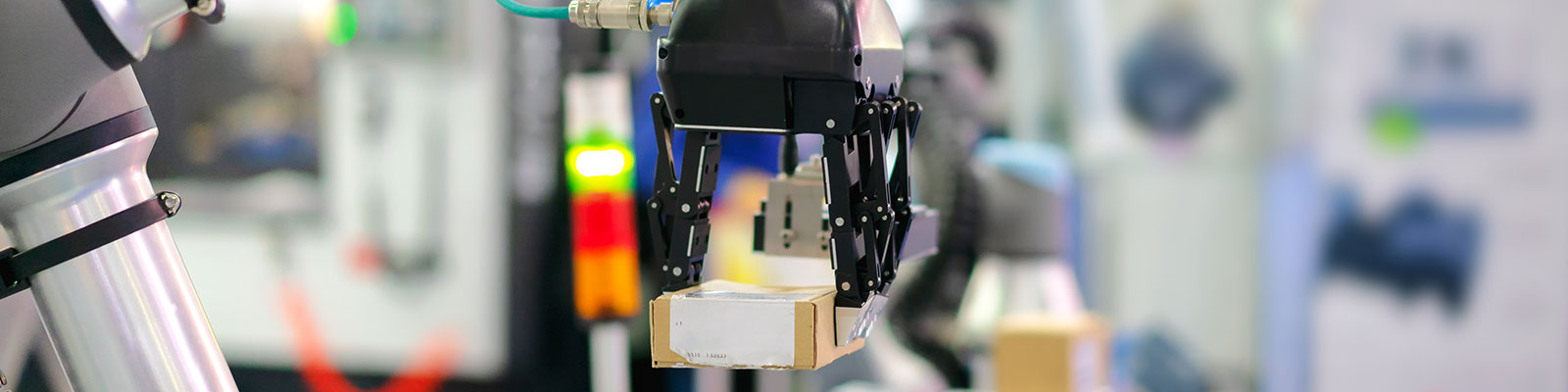
In Industrie 4.0 factories, smart machines control production processes by themselves. Service robots help people do physically demanding work in the assembly shop. Driverless transport vehicles manage the logistics processes and the flow of materials without any human intervention. But it is not only ‘smart factories’ that are becoming increasingly connected. Across company and industry borders, a wide range of economic stakeholders are also becoming part of this trend: from medium-sized logistics companies to specialised technical service providers and creative start-ups.
Producing in a more flexible, customised and efficient way
The use of digital technologies in industry will lead to the development of a large number of new production methods, business models and products. For example, production lines need no longer be limited to a single product. This will change the demands made of industrial manufacturing. IT support will make it possible to dynamically adapt processing stations to a changing product mix. This means capacity can be used in the best way possible. In addition, the automated analysis processes that are used can reveal maintenance needs and production downtime risks.
Cooperation: working together to harness new opportunities
This offers enormous potential for innovation and business in Germany, as some 15 million jobs depend directly and indirectly on the manufacturing industries. The digitalisation of industry will not only transform value-creation processes but also give rise to new business models and new prospects for employees. Smart, digital production processes present great opportunities for businesses – particularly for SMEs.
However, as industry becomes more digitalised and connected, the number of interfaces and the amount of data that is exchanged will increase. Unified standards, IT security and data protection therefore play a crucial role. However, such transversal issues cannot be dealt with by one single company or industry. Only if all the relevant stakeholders from industry, academia, politics and society are heard and if they work together as partners from an early stage onwards can we make the fourth industrial revolution a success.
Key social and political organisational tasks
The German government wants to utilise the enormous potential of Industrie 4.0 to strengthen Germany’s manufacturing base. Smart, digital production processes present great opportunities for businesses – particularly for SMEs.
Industrie 4.0 is a central focus of the Federal Government’s Digital Agenda. In the two funding programmes entitled ‘Autonomics for Industrie 4.0’ and ‘Smart Service World’, the Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action is already providing close to €100 million to foster research and innovation in the field of Industrie 4.0.